Chemical structure:
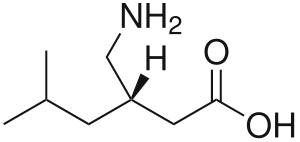
IUPAC name:
(3S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid
CAS number:
148553-50-8
Therapy area:
Anti-Convulsant
References:
IP/USP
Status:
Commercial scale
Mechanism of action
Pregabalin’s method of action for reducing pain: Pregabalin inhibits the VDCC, which reduces Ca2+ influx and, as a result, the release of glutamate and sensory neuropeptides (substance P and CGRP) at synapses. Pregabalin causes an increase in the activity of EAATs (excitatory amino acid transporters), which results in a greater reduction in glutamate synaptic availability. Reduced glutamate levels further prevented NMDA from activating and reduced neuronal activity. In addition, Pregabalin opens the KATP channels, which also helps to reduce neuronal excitement. Pregabalin across all these routes finally gives considerable pain relief in diverse neuropathic pain conditions.
DISCLAIMER: PRODUCTS COVERED BY VALID & UNEXPIRED PATENTS ARE NOT OFFERED (OR) SUPPLIED FOR COMMERCIAL SCALE. THE PATENT POSITION SHOULD BE VERIFIED & LIABILITY LIES WITH THE CUSTOMER ONLY. PRODUCTS COVERED BY PATENTS ARE AVAILABLE ONLY FOR R&D USE.


